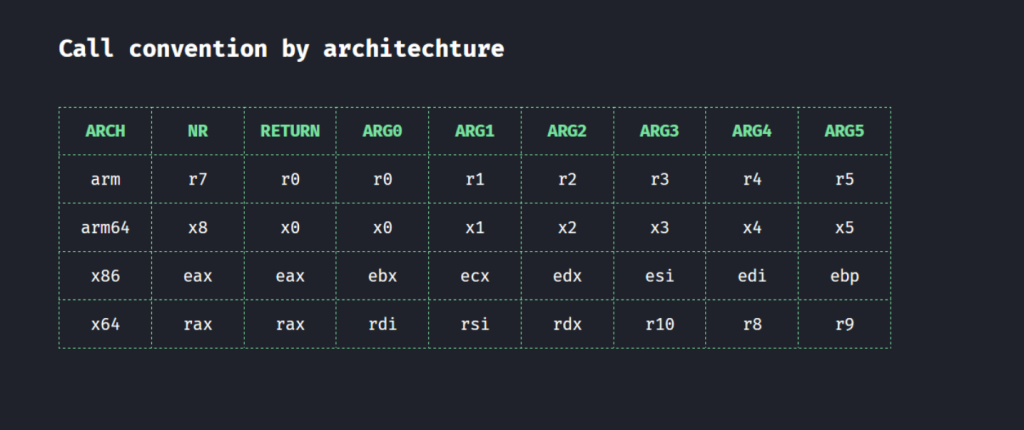
ADB常用指令
//连接模拟器 5555(我的高版本安卓) 或者 5557 端口
adb connect 127.0.0.1:5555
//查看设备
adb devices
//多于一个设备连接
adb -s 设备ID shell
//断开指定设备
adb disconnect 设备ID
//杀死当前adb服务
adb kill-server
//重启adb服务
adb strat-server
//下载、install文件到指定的设备
adb -s 设备ID push local_file file_target (install 123.apk)
//转发监听
adb forward tcp:23946 tcp:23946脱UPX壳
先放到程序入口点(四个push)
然后运行之后在栈的内存窗口处下硬件断点(访问)rsp
脱壳的时候到主程序的时候会有一个 sub rsp,28(OEP) 然后一个call,
然后一个add rsp,28,然后跳到主程序
在od中用S dump出来然后需要fix一下dump
如果要修复一下让程序能执行,就在ida里面调到VA + size的地方手动找到
应该导入的最后一个函数的位置,使他识别的长度是对的
在ida中也是一样的操作,下断点,进jmp函数之后按P直接创建函数
然后看return了那个变量,然后那个变量等于的就是主函数
在IDE里面看到上面这种编译的环境可以看看是否是pyinstxtractor.py可以解包的文件,或者扔进ida里面可以很明显的看到有python的丑陋的代码
OLLVM反混淆
该模块利用了angr的符号执行来还原函数,需要提前进入angr的环境
环境已创建只需要进入虚拟环境即可,如果重新创建会导致python安装的angr被清空
cd angrfile
python3 deflat.py filename start_address #函数地址 老版本
python deflat.py -f filename --addr start_address #新版
搭配 ida python 食用效果更佳
IDA Python
ida python以下内容大部分学习这位大佬的文章,个人感觉总结的不错
获取地址
idc.here()或 idc.get_screen_ea():取当前地址ida_ida.inf_get_min_ea():获取最小地址(可以使用的)ida_ida.inf_get_max_ea():获取最大地址(可以使用的)idc.read_selection_start():获取所选范围的起始地址idc.read_selection_end():获取所选范围的结束地址idc.get_name_ea_simple(name):获取名称对应的地址,如果获取不到则返回 ida_idaapi.BADADDR
获取某地址的值
idc.get_wide_byte(addr):以 1 字节为单位获取地址处的值idc.get_wide_word(addr):以 2 字节(字)的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_wide_dword(addr):以 4 字节的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_qword(addr):以 8 字节的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_bytes(addr, len):获取addr地址处len长度的数据'\x00'结尾的bytes类型数据转换为字符串的方法idc.get_bytes(addr, idc.get_item_size(addr)).decode('utf-8').rstrip('\x00')
idc.get_item_size(addr):获取addr地址处的数据大小,例如汇编指令长度
修改地址处的值
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr, value):修改addr地址的值为value,每次修改 1 个字节ida_bytes.patch_word(addr, value):每次修改 2 个字节ida_bytes.patch_dword(addr, value):每次修改 4 个字节ida_bytes.patch_qword(addr, value):每次修改 8 个字节idc.patch_bytes(addr, data):在addr地址处写入data(bytes类型数据)
修改地址的类型
idc.del_items(addr):去除目标地址处数据的属性 类似于 Uidc.create_insn(addr):将目标地址处的数据设置为代码,类似于C 有可能会失败,可以与ida_name.set_name(addr, '')配合来避免失败
汇编指令操作
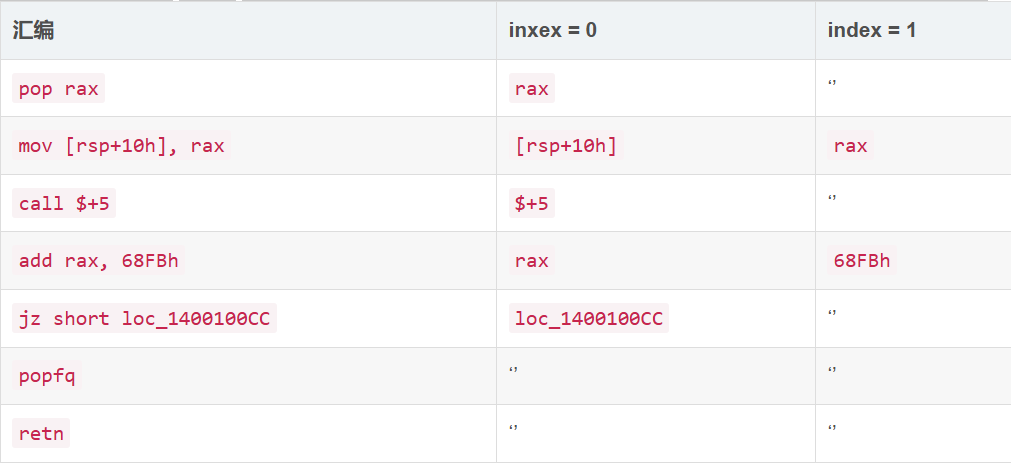
idc.GetDisasm(addr)或idc.generate_disasm_line(addr,flags):获取地址处的汇编语句,这里flags通常为 0idc.print_operand(addr,index):获取指定地址addr的汇编指令的第index个操作数(字符串形式),如果index索引超过操作数的个数则返回空字符串。下面简单举几个例子感受一下
idc.get_operand_type(addr, index):获取操作数的类型o_void:无效操作数,表示没有操作数o_reg:寄存器操作数,表示一个寄存器o_mem:内存操作数,表示一个内存地址o_phrase:短语操作数,表示根据寄存器和偏移量计算的内存地址o_displ:带偏移量的内存操作数,表示根据寄存器、偏移量和可选标志寄存器计算的内存地址o_imm:立即数操作数,表示一个立即数值o_far:远跳转操作数,表示一个远跳转地址o_near:相对跳转操作数,表示一个相对于当前指令地址的跳转地址
idc.get_operand_value(addr, index):获取指定索引操作数中的值。- 对于寄存器操作数
(o_reg),返回寄存器的编号 - 对于内存操作数
(o_mem),返回内存地址的值 - 对于立即数操作数
(o_imm),返回立即数的值 - 对于相对跳转操作数 (
o_near),返回跳转的地址 - 对于其他特定于处理器的操作数类型,返回相应的值,具体含义需要参考相关文档
- 对于寄存器操作数
idc.print_insn_mnem(addr):获取指定地址addr的汇编指令的操作指令(如 mov、add)idc.next_head(addr):获取当前地址的汇编的下一条汇编的地址。idc.prev_head(addr):获取当前地址的汇编的上一条汇编的地址
段操作
idc.get_segm_name(addr):获取地址addr所在段的名字(参数为当前的地址)idc.get_segm_start(addr):获取地址addr所在段的开始地址idc.get_segm_end(addr):获取地址addr所在段的结束地址idc.get_first_seg():获取第一个段的地址idc.get_next_seg(addr):获取地址大于addr的第一个段的起始地址idautil.Segments():返回一个列表记录所有段的地址
#遍历所有段的代码
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
for seg_addr in idautils.Segments():
segname = idc.get_segm_name(seg_addr)
segstart = idc.get_segm_start(seg_addr)
segend = idc.get_segm_end(seg_addr)
print("段名:" + segname + " 起始地址:" + hex(segstart) + " 结束地址:" + hex(segend));函数操作
idautils.Functions(startaddr,endaddr):获取指定地址之间的所有函数idc.get_func_name(addr):获取指定地址所在函数的函数名get_func_cmt(addr, repeatable):获取函数的注释repeatable:0 是获取常规注释,1 是获取重复注释
idc.set_func_cmt(ea, cmt, repeatable):设置函数注释idc.choose_func(title):弹出选择框要求用户进行选择函数,返回值为用户选择的函数的地址,若直接关闭选择框则返回值为 0xffffffffffffffffidc.get_func_off_str(addr):寻找函数结尾,如果函数存在则返回结尾地址,否则返回BADADDRida_funcs.set_func_end(addr, newend):设置函数结尾为newendida_funcs.set_func_start(addr, newstart):设置函数开头为newstartidc.set_name(addr, name):设置地址处的名字为nameida_funcs.get_func(addr).start_ea:获取addr所在函数的地址idc.get_prev_func(addr):获取addr所在函数的前一个函数的地址idc.get_next_func(addr):获取addr所在函数的后一个函数的地址ida_funcs.add_func(addr):在addr地址创建函数
#遍历.text段上所有的函数
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
for seg in idautils.Segments():
segname = idc.get_segm_name(seg)
segstart = idc.get_segm_start(seg)
segend = idc.get_segm_end(seg)
if (segname == '.text'):
for funcaddr in Functions(segstart,segend):
funname = idc.get_func_name(funcaddr)
funend = idc.find_func_end(funcaddr)
funnext = idc.get_next_func(funcaddr)
funnextname = idc.get_func_name(funnext)
print("当前函数名: " + funname + "当前结束地址: " + hex(funend) +"下一个函数地址: " + hex(funnext) + "下一个函数名: " + funnextname)数据查询
idc.find_binary(ea, flag, searchstr, radix=16):查找二进制找到返回地址没找到返回 -1 (BADADDR)flags:搜索标志SEARCH_DOWN:向下搜索SEARCH_UP:向上搜索SEARCH_NEXT:获取下一个找到的对象SEARCH_CASE:指定大小写敏感度SEARCH_UNICODE:搜索 Unicode 字符串
searchstr:要搜索的二进制模式或指令序列,例如E8 00 00 00 00 58。radix:模式中数字的基数,默认为十六进制
ida_search.find_data(ea, sflag):从ea开始寻找下一个数据地址ida_search.find_code(ea, sflag):从ea开始寻找下一个代码地址ida_kernwin.jumpto(ea):跳转到ea位置
数据校验函数
ida_bytes.get_full_flags(ea):获取ea地址处的标志,其中包含了ea地址处的相关属性ida_bytes.is_code(f):判断是否为代码,其中f为获取的标志位ida_bytes.is_data(f):判断是否为数据,其中f为获取的标志位ida_bytes.del_items(ea):删除ea地址处的类型
交叉引用(X)
idautils.CodeRefsTo(ea, flow):获取引用ea地址处的内容的地址。其中flow表示代码顺序执行的是否计算在内,比如如果flow = True那么认为当前指令的上一条指令引用了当前指令idautils.CodeRefsFrom(ea, flow):ea地址处的代码引用了何处的代码。idautils.DataRefsTo(ea):获取引用ea地址处的内容的地址idautils.DataRefsFrom(ea):ea地址处的代码引用了何处的数据
几个实际应用
#做题的时候遇到的一个比较简单的脚本,学到这应该是可以看懂这个脚本了
st = 0x0000000000400620 #main开始
end = 0x0000000000402144 #main结束
def patch_nop(start,end):
for i in range(start,end):
ida_bytes.patch_byte(i, 0x90)
def next_instr(addr):
return addr+idc.get_item_size(addr)
#获取指令或数据长度,这个函数的作用就是去往下一条指令
addr = st
while(addr<end):
next = next_instr(addr)
if "ds:dword_603054" in GetDisasm(addr):
#GetDisasm(addr)得到addr的反汇编语句 l类型是str
while(True):
addr = next
next = next_instr(addr)
if "jnz" in GetDisasm(addr):
dest = idc.get_operand_value(addr, 0) #得到操作数,就是指令后的数
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr, 0xe9) #0xe9 jmp后面的四个字节是偏移
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr+5, 0x90) #nop第五个字节
offset = dest - (addr + 5)
#调整为正确的偏移地址 也就是相对偏移地址 - 当前指令后的地址
ida_bytes.patch_dword(addr + 1, offset) #把地址赋值给jmp后
print("patch bcf: 0x%x"%addr)
addr = next
break
else:
addr = next解密
来杯下午茶吗?
TEA
#include <stdint.h>
void encrypt (uint32_t* v, uint32_t* k) {
uint32_t v0=v[0], v1=v[1], sum=0, i; /* set up */
uint32_t delta=0x9e3779b9; /* a key schedule constant */
uint32_t k0=k[0], k1=k[1], k2=k[2], k3=k[3]; /* cache key */
for (i=0; i < 32; i++) { /* basic cycle start */
sum += delta;
v0 += ((v1<<4) + k0) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1>>5) + k1);
v1 += ((v0<<4) + k2) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0>>5) + k3);
} /* end cycle */
v[0]=v0; v[1]=v1;
}
void decrypt (uint32_t* v, uint32_t* k) {
uint32_t v0=v[0], v1=v[1], sum=0xC6EF3720, i; /* set up */
uint32_t delta=0x9e3779b9; /* a key schedule constant */
uint32_t k0=k[0], k1=k[1], k2=k[2], k3=k[3]; /* cache key */
for (i=0; i<32; i++) { /* basic cycle start */
v1 -= ((v0<<4) + k2) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0>>5) + k3);
v0 -= ((v1<<4) + k0) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1>>5) + k1);
sum -= delta;
} /* end cycle */
v[0]=v0; v[1]=v1;
}XTEA
#include <stdint.h>
/* take 64 bits of data in v[0] and v[1] and 128 bits of key[0] - key[3] */
void encipher(unsigned int num_rounds, uint32_t v[2], uint32_t const key[4]) {
unsigned int i;
uint32_t v0=v[0], v1=v[1], sum=0, delta=0x9E3779B9;
for (i=0; i < num_rounds; i++) {
v0 += (((v1 << 4) ^ (v1 >> 5)) + v1) ^ (sum + key[sum & 3]);
sum += delta;
v1 += (((v0 << 4) ^ (v0 >> 5)) + v0) ^ (sum + key[(sum>>11) & 3]);
}
v[0]=v0; v[1]=v1;
}
void decipher(unsigned int num_rounds, uint32_t v[2], uint32_t const key[4]) {
unsigned int i;
uint32_t v0=v[0], v1=v[1], delta=0x9E3779B9, sum=delta*num_rounds;
for (i=0; i < num_rounds; i++) {
v1 -= (((v0 << 4) ^ (v0 >> 5)) + v0) ^ (sum + key[(sum>>11) & 3]);
sum -= delta;
v0 -= (((v1 << 4) ^ (v1 >> 5)) + v1) ^ (sum + key[sum & 3]);
}
v[0]=v0; v[1]=v1;
}XXTEA
#define DELTA 0x9e3779b9
#define MX ((z>>5^y<<2) + (y>>3^z<<4) ^ (sum^y) + (k[p&3^e]^z))
long btea(long* v, long n, long* k) {
unsigned long z=v[n-1], y=v[0], sum=0, e;
long p, q ;
if (n > 1) { /* Coding Part */
q = 6 + 52/n;
while (q-- > 0) {
sum += DELTA;
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=0; p<n-1; p++) y = v[p+1], z = v[p] += MX;
y = v[0];
z = v[n-1] += MX;
}
return 0 ;
} else if (n < -1) { /* Decoding Part */
n = -n;
q = 6 + 52/n;
sum = q*DELTA ;
while (sum != 0) {
e = (sum >> 2) & 3;
for (p=n-1; p>0; p--) z = v[p-1], y = v[p] -= MX;
z = v[n-1];
y = v[0] -= MX;
sum -= DELTA;
}
return 0;
}
return 1;
}对称加密
包含AES(EBC、CBC)、DES(EBC、CBC)、SM4
AES
数据十六字节为单位,key为16、24、32字节,iv为16字节
pkcs7填充 缺几位就补什么,六位补(06 06 06 06 06 06) 、zero填充补 00
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def encrypt_ECB(data,key):
cipher = AES.new(key,AES.MODE_ECB)
encrypt_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypt_data
def decrypt_ECB(data,key):
cipher = AES.new(key,AES.MODE_ECB)
decrypt_data = cipher.decrypt(data)
return decrypt_data
def encrypt_CBC(data,key,iv):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC,iv)
encrypt_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypt_data
def decrypt_CBC(data,key,iv):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC,iv)
decrypt_data = cipher.decrypt(data)
return decrypt_data
def pad(source,num,padding): #byte的数据要求num对齐,以padding(byte)为弥补
while len(source)%num:
source += padding
return source
if __name__ =='__main__':
data = b'flag{114514}'
key = b'5201314ErrorAiLa'
iv = b'WelcomeToReverse'
data = pad(data,16,b'\0')
encrypt_data = encrypt_ECB(data,key)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = decrypt_ECB(encrypt_data,key)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)
encrypt_data = encrypt_CBC(data,key,iv)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = decrypt_CBC(encrypt_data,key,iv)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)DES
加解密与AES类似,key和iv都要求是8字节(64bits),数据是16字节为单位
from Crypto.Cipher import DES
def encrypt_ECB(data,key):
cipher = DES.new(key,DES.MODE_ECB)
encrypt_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypt_data
def decrypt_ECB(data,key):
cipher = DES.new(key,DES.MODE_ECB)
decrypt_data = cipher.decrypt(data)
return decrypt_data
def encrypt_CBC(data,key,iv):
cipher = DES.new(key, DES.MODE_CBC,iv)
encrypt_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypt_data
def decrypt_CBC(data,key,iv):
cipher = DES.new(key, DES.MODE_CBC,iv)
decrypt_data = cipher.decrypt(data)
return decrypt_data
def pad(source,num,padding): #byte的数据要求num对齐,以padding为弥补
while len(source)%num:
source += padding
return source
if __name__ =='__main__':
data = b'flag{114514}'
key = b'520Error'
iv = b'Reverse!'
data = pad(data,16,b'\0')
encrypt_data = encrypt_ECB(data,key)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = decrypt_ECB(encrypt_data,key)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)
encrypt_data = encrypt_CBC(data,key,iv)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = decrypt_CBC(encrypt_data,key,iv)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)通常情况下数据长度为16字节为一组(128bits)、key为16字节(128bits),iv也是16字节(128bits)
SM4
from gmssl import sm4
def sm4_encrypt(data,key):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4()
cipher.set_key(key,sm4.SM4_ENCRYPT)
encrypt_data = cipher.crypt_ecb(data)
return encrypt_data
def sm4_decrypt(data,key):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4()
cipher.set_key(key,sm4.SM4_DECRYPT)
decrypt_data = cipher.crypt_ecb(data)
return decrypt_data
def sm4_encrypt_cbc(data,key,iv):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4()
cipher.set_key(key,sm4.SM4_ENCRYPT)
encrypt_data = cipher.crypt_cbc(iv,data)
return encrypt_data
def sm4_decrypt_cbc(data,key,iv):
cipher = sm4.CryptSM4()
cipher.set_key(key,sm4.SM4_DECRYPT)
decrypt_data = cipher.crypt_cbc(iv,data)
return decrypt_data
def pad(source,num,padding = None): #byte的数据要求num对齐,以padding为弥补
if padding == None:
padding = (len(source)%num).to_bytes()
while len(source)%num:
source += padding
else:
while len(source)%num:
source += padding
return source
if __name__ =='__main__':
data = b'flag{114514}'
key = b'5201314ErrorAiLa'
iv = b'WelcomeToReverse'
pad(data,16)
encrypt_data = sm4_encrypt(data,key)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = sm4_decrypt(encrypt_data,key)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)
encrypt_data = sm4_encrypt_cbc(data,key,iv)
print('After Encrypt: ', encrypt_data)
decrypt_data = sm4_decrypt_cbc(encrypt_data,key,iv)
print('After Decrypt :', decrypt_data)CRC
64
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int v11 = 255;
long long v10 = ((long long*)end)[i];
do
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (v10 & 0x1 == 1)//xor,高位是1
{
v10 = (v10 ^ 0x71234EA7D92996F5LL) >> 1;
v10 |= 0x8000000000000000;
}
else
{
v10 /= 2;
v10 &= 0x7fffffffffffffff;
}
}
v11 -= 5;
} while (v11);
((long long*)a)[i] = v10;
}32
uint32_t crc32(const void* buf, size_t size) {
const uint8_t* p = buf;
uint32_t crc = ~0U;
while (size--) {
crc = crc32_tab[(crc ^ *p++) & 0xFF] ^ (crc >> 8);
}
return ~crc;
}
uint crc32(byte *data, int size)
{
uint r = ~0; byte *end = data + size;
while(data < end)
{
r ^= *data++;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
uint t = ~((r&1) — 1); r = (r>>1) ^ (0xEDB88320 & t);
}
}
return ~r;
}RC4
/*初始化函数*/
void rc4_init(unsigned char *s, unsigned char *key, unsigned long Len) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
char k[256] = {0};
unsigned char tmp = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
s[i] = i;
k[i] = key[i % Len];
}
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
j = (j + s[i] + k[i]) % 256;
tmp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j]; // 交换s[i]和s[j]
s[j] = tmp;
}
}
/*加解密*/
void rc4_crypt(unsigned char *s, unsigned char *Data, unsigned long Len) {
int i = 0, j = 0, t = 0;
unsigned long k = 0;
unsigned char tmp;
for (k = 0; k < Len; k++) {
i = (i + 1) % 256;
j = (j + s[i]) % 256;
tmp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j]; // 交换s[x]和s[y]
s[j] = tmp;
t = (s[i] + s[j]) % 256;
Data[k] ^= s[t];
}
}Salsa20 和 ChaCha20
两者都是与明文进行异或操作
Salsa20
通过16或者32位的key和8位的iv产生与明文进行异或的密钥流
密钥扩展如下(原理不是很懂)
# key 为 32 字节时c[0] + key[0:16] + c[1] + iv + 计数器(8 bytes) + key[16:32] + c[4]c = [0x61707865, 0x3320646e, 0x79622d32, 0x6b206574] # expand 32-byte k# key 为 16 字节时c[0] + key[0:16] + c[1] + iv + 计数器(8 bytes) + key[0:16] + c[4]c = [0x61707865, 0x3120646e, 0x79622d36, 0x6b206574] # expand 16-byte k核心逻辑
#define R(a,b) (((a) << (b)) | ((a) >> (32 - (b))))
void salsa20_word_specification(uint32 out[16],uint32 in[16])
{
int i;
uint32 x[16];
for (i = 0; i < 16; ++i) x[i] = in[i];
for (i = 20; i > 0; i -= 2) { // 迭代次数,注意每次 i -= 2 !
// 每列
x[ 4] ^= R(x[ 0]+x[12], 7); x[ 8] ^= R(x[ 4]+x[ 0], 9);
x[12] ^= R(x[ 8]+x[ 4],13); x[ 0] ^= R(x[12]+x[ 8],18);
x[ 9] ^= R(x[ 5]+x[ 1], 7); x[13] ^= R(x[ 9]+x[ 5], 9);
x[ 1] ^= R(x[13]+x[ 9],13); x[ 5] ^= R(x[ 1]+x[13],18);
x[14] ^= R(x[10]+x[ 6], 7); x[ 2] ^= R(x[14]+x[10], 9);
x[ 6] ^= R(x[ 2]+x[14],13); x[10] ^= R(x[ 6]+x[ 2],18);
x[ 3] ^= R(x[15]+x[11], 7); x[ 7] ^= R(x[ 3]+x[15], 9);
x[11] ^= R(x[ 7]+x[ 3],13); x[15] ^= R(x[11]+x[ 7],18);
// 每行
x[ 1] ^= R(x[ 0]+x[ 3], 7); x[ 2] ^= R(x[ 1]+x[ 0], 9);
x[ 3] ^= R(x[ 2]+x[ 1],13); x[ 0] ^= R(x[ 3]+x[ 2],18);
x[ 6] ^= R(x[ 5]+x[ 4], 7); x[ 7] ^= R(x[ 6]+x[ 5], 9);
x[ 4] ^= R(x[ 7]+x[ 6],13); x[ 5] ^= R(x[ 4]+x[ 7],18);
x[11] ^= R(x[10]+x[ 9], 7); x[ 8] ^= R(x[11]+x[10], 9);
x[ 9] ^= R(x[ 8]+x[11],13); x[10] ^= R(x[ 9]+x[ 8],18);
x[12] ^= R(x[15]+x[14], 7); x[13] ^= R(x[12]+x[15], 9);
x[14] ^= R(x[13]+x[12],13); x[15] ^= R(x[14]+x[13],18);
}
for (i = 0;i < 16;++i) out[i] = x[i] + in[i];
}然后与明文异或
标志性的循环左移 7 9 13 18 到时会四个一组进行处理,其中的20轮也可魔改
ChaCha20
密钥扩展规则如下
c[0:4] + key[0:32] + 计数器(4 bytes) + iv
c = [0x61707865, 0x3320646e, 0x79622d32, 0x6b206574] # expand 32-byte k密钥32 位 iv 12字节
static inline void u32t8le(uint32_t v, uint8_t p[4]) {
p[0] = v & 0xff;
p[1] = (v >> 8) & 0xff;
p[2] = (v >> 16) & 0xff;
p[3] = (v >> 24) & 0xff;
}
static inline uint32_t u8t32le(uint8_t p[4]) {
uint32_t value = p[3];
value = (value << 8) | p[2];
value = (value << 8) | p[1];
value = (value << 8) | p[0];
return value;
}
static inline uint32_t rotl32(uint32_t x, int n) {
// http://blog.regehr.org/archives/1063
return x << n | (x >> (-n & 31));
}
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7539#section-2.1
static void chacha20_quarterround(uint32_t *x, int a, int b, int c, int d) {
x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 16);
x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 12);
x[a] += x[b]; x[d] = rotl32(x[d] ^ x[a], 8);
x[c] += x[d]; x[b] = rotl32(x[b] ^ x[c], 7);
}
static void chacha20_serialize(uint32_t in[16], uint8_t output[64]) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
u32t8le(in[i], output + (i << 2));
}
}
static void chacha20_block(uint32_t in[16], uint8_t out[64], int num_rounds) {
int i;
uint32_t x[16];
memcpy(x, in, sizeof(uint32_t) * 16);
for (i = num_rounds; i > 0; i -= 2) {
chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 4, 8, 12);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 5, 9, 13);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 6, 10, 14);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 7, 11, 15);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 0, 5, 10, 15);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 1, 6, 11, 12);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 2, 7, 8, 13);
chacha20_quarterround(x, 3, 4, 9, 14);
}
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
x[i] += in[i];
}
chacha20_serialize(x, out);
}标志性的循环左移16 12 8 7 可以以此来识别,实际使用中也可能将密钥扩展那一步直接写死为扩展后的
变表C解密
base码表
Base16 编码表:0123456789ABCDEF
Base32 编码表:ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567
Base58 编码表:123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyz
Base62 编码表:0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
Base64 编码表:ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/
Base85 编码表:!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
Base91 编码表:ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789!#$%&()*+,./:;<=>?@[]^_`{|}~"变Sbox_AES_EBC
#include <stdio.h>
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
/*
* @Author:timerring
* @Date: 2021-11-08 21:59:11
* @LastEditTime: 2021-11-12 23:44:19
* @FilePath:c:\Users\timerring\AES.cpp
*/
//定义轮常量表
static const unsigned char Rcon[10] = {
0x01,0x02,0x04,0x08,0x10,0x20,0x40,0x80,0x1b,0x36 };
//定义有限域*2乘法
static unsigned char x2time(unsigned char x)
{
if (x & 0x80)
{
return (((x << 1) ^ 0x1B) & 0xFF);
}
return x << 1;
}
//定义有限域*3乘法
static unsigned char x3time(unsigned char x)
{
return (x2time(x) ^ x);
}
//定义有限域*4乘法
static unsigned char x4time(unsigned char x)
{
return (x2time(x2time(x)));
}
//定义有限域*8乘法
static unsigned char x8time(unsigned char x)
{
return (x2time(x2time(x2time(x))));
}
//定义有限域*9乘法
static unsigned char x9time(unsigned char x)
{
return (x8time(x) ^ x);
}
//定义有限域*B乘法
static unsigned char xBtime(unsigned char x)
{
return (x8time(x) ^ x2time(x) ^ x);
}
//定义有限域*D乘法
static unsigned char xDtime(unsigned char x)
{
return (x8time(x) ^ x4time(x) ^ x);
}
//定义有限域*E乘法
static unsigned char xEtime(unsigned char x)
{
return (x8time(x) ^ x4time(x) ^ x2time(x));
}
//s盒矩阵 Substitution Table
static const unsigned char sbox[256] = {
124, 202, 123, 119, 242, 107, 111, 197, 48, 1, 103, 43, 254, 215, 71, 171, 118, 99, 130, 201, 125, 250, 89, 240, 173, 212, 162, 175, 156, 164, 114, 192, 183, 253, 147, 38, 54, 63, 247, 204, 52, 165, 229, 241, 113, 216, 49, 21, 4, 199, 35, 195, 24, 150, 5, 154, 7, 18, 128, 226, 235, 39, 178, 117, 9, 131, 44, 26, 27, 110, 90, 160, 82, 59, 214, 179, 41, 227, 47, 132, 83, 209, 0, 237, 32, 252, 177, 91, 106, 203, 190, 57, 74, 76, 88, 207, 208, 239, 170, 251, 67, 77, 51, 133, 69, 249, 2, 127, 80, 60, 159, 168, 81, 163, 64, 143, 146, 157, 56, 245, 188, 182, 218, 33, 16, 255, 243, 210, 151, 205, 12, 19, 236, 95, 68, 23, 196, 167, 126, 61, 100, 93, 25, 115, 96, 129, 79, 220, 34, 42, 144, 136, 70, 238, 184, 20, 222, 94, 11, 219, 224, 50, 58, 10, 73, 6, 36, 92, 194, 211, 172, 98, 145, 149, 228, 121, 231, 200, 55, 109, 141, 213, 78, 169, 108, 86, 244, 234, 101, 122, 174, 8, 186, 120, 37, 46, 28, 166, 180, 198, 232, 221, 116, 31, 75, 189, 139, 138, 112, 62, 181, 102, 72, 3, 246, 14, 97, 53, 87, 185, 134, 193, 29, 158, 225, 248, 152, 17, 105, 217, 142, 148, 155, 30, 233, 206, 85, 40, 223, 140, 161, 137, 13, 191, 230, 66, 104, 65, 153, 45, 15, 176, 84, 187, 22, 135
};
//逆向S盒矩阵
static const unsigned char contrary_sbox[256] = {
82, 9, 106, 213, 48, 54, 165, 56, 191, 64, 163, 158, 130, 242, 215, 250, 124, 227, 57, 131, 155, 47, 254, 135, 52, 142, 67, 68, 196, 222, 233, 203, 84, 123, 148, 50, 166, 194, 35, 61, 237, 76, 149, 11, 66, 249, 195, 78, 8, 46, 161, 102, 40, 217, 36, 178, 118, 91, 162, 73, 109, 139, 209, 37, 114, 247, 245, 100, 134, 104, 152, 14, 212, 164, 92, 204, 93, 101, 182, 146, 108, 112, 72, 80, 252, 236, 185, 218, 94, 22, 70, 87, 167, 141, 157, 133, 144, 216, 171, 17, 140, 188, 211, 10, 246, 228, 88, 5, 184, 179, 69, 6, 208, 44, 30, 143, 202, 63, 16, 3, 193, 175, 189, 2, 0, 20, 138, 107, 58, 145, 18, 65, 79, 103, 220, 255, 151, 241, 207, 206, 239, 180, 230, 115, 150, 172, 116, 34, 231, 173, 53, 128, 226, 248, 55, 232, 28, 117, 223, 110, 71, 240, 26, 113, 29, 41, 197, 137, 111, 183, 98, 15, 170, 24, 190, 27, 251, 86, 62, 75, 198, 210, 121, 32, 154, 219, 192, 253, 120, 205, 90, 243, 31, 221, 168, 51, 136, 7, 199, 49, 177, 19, 1, 89, 39, 129, 235, 95, 96, 81, 127, 169, 25, 181, 74, 13, 45, 229, 122, 159, 147, 201, 156, 238, 160, 224, 59, 77, 174, 42, 244, 176, 200, 234, 187, 60, 132, 83, 153, 97, 23, 43, 4, 126, 186, 119, 214, 38, 225, 105, 21, 99, 85, 33, 12, 125
};
//定义列混合操作
static void MixColumns(unsigned char* col)
{
unsigned char tmp[4], xt[4];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++, col += 4)
{ //col代表一列的基地址,col+4:下一列的基地址
//xt[n]代表*2 xt[n]^col[n]代表*3 col[n]代表*1
tmp[0] = x2time(col[0]) ^ x3time(col[1]) ^ col[2] ^ col[3]; //2 3 1 1
tmp[1] = col[0] ^ x2time(col[1]) ^ x3time(col[2]) ^ col[3]; //1 2 3 1
tmp[2] = col[0] ^ col[1] ^ x2time(col[2]) ^ x3time(col[3]); //1 1 2 3
tmp[3] = x3time(col[0]) ^ col[1] ^ col[2] ^ x2time(col[3]); //3 1 1 2
//修改后的值 直接在原矩阵上修改
col[0] = tmp[0];
col[1] = tmp[1];
col[2] = tmp[2];
col[3] = tmp[3];
}
}
//定义逆向列混淆
static void Contrary_MixColumns(unsigned char* col)
{
unsigned char tmp[4];
unsigned char xt2[4];//colx2
unsigned char xt4[4];//colx4
unsigned char xt8[4];//colx8
int x;
for (x = 0; x < 4; x++, col += 4)
{
tmp[0] = xEtime(col[0]) ^ xBtime(col[1]) ^ xDtime(col[2]) ^ x9time(col[3]);
tmp[1] = x9time(col[0]) ^ xEtime(col[1]) ^ xBtime(col[2]) ^ xDtime(col[3]);
tmp[2] = xDtime(col[0]) ^ x9time(col[1]) ^ xEtime(col[2]) ^ xBtime(col[3]);
tmp[3] = xBtime(col[0]) ^ xDtime(col[1]) ^ x9time(col[2]) ^ xEtime(col[3]);
col[0] = tmp[0];
col[1] = tmp[1];
col[2] = tmp[2];
col[3] = tmp[3];
}
}
//定义行移位操作:行左循环移位
static void ShiftRows(unsigned char* col)
{//正向行移位
unsigned char t;
//左移1位
t = col[1]; col[1] = col[5]; col[5] = col[9]; col[9] = col[13]; col[13] = t;
//左移2位,交换2次数字来实现
t = col[2]; col[2] = col[10]; col[10] = t;
t = col[6]; col[6] = col[14]; col[14] = t;
//左移3位,相当于右移1次
t = col[15]; col[15] = col[11]; col[11] = col[7]; col[7] = col[3]; col[3] = t;
//第4行不移位
}
//逆向行移位
static void Contrary_ShiftRows(unsigned char* col)
{
unsigned char t;
t = col[13]; col[13] = col[9]; col[9] = col[5]; col[5] = col[1]; col[1] = t;
t = col[2]; col[2] = col[10]; col[10] = t;
t = col[6]; col[6] = col[14]; col[14] = t;
t = col[3]; col[3] = col[7]; col[7] = col[11]; col[11] = col[15]; col[15] = t;
//同理,第4行不移位
}
//定义s盒字节代换替换操作
static void SubBytes(unsigned char* col)
{//字节代换
int x;
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++)
{
col[x] = sbox[col[x]];
}
}
//逆向字节代换
static void Contrary_SubBytes(unsigned char* col)
{
int x;
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++)
{
col[x] = contrary_sbox[col[x]];
}
}
//密钥编排,16字节--->44列32bit密钥生成--> 11组16字节:分别用于11轮 轮密钥加运算
void ScheduleKey(unsigned char* inkey, unsigned char* outkey, int Nk, int Nr)
{
//inkey:初始16字节密钥key
//outkey:11组*16字节扩展密钥expansionkey
//Nk:4列
//Nr:10轮round
unsigned char temp[4], t;
int x, i;
/*copy the key*/
//第0组:[0-3]直接拷贝
for (i = 0; i < (4 * Nk); i++)
{
outkey[i] = inkey[i];
}
//第1-10组:[4-43]
i = Nk;
while (i < (4 * (Nr + 1))) //i=4~43 WORD 32bit的首字节地址,每一个4字节
{//1次循环生成1个字节扩展密钥,4次循环生成一个WORD
//temp:4字节数组:代表一个WORD密钥
//i不是4的倍数的时候
//每个temp = 每个outkey32bit = 4字节
for (x = 0; x < 4; x++)
temp[x] = outkey[(4 * (i - 1)) + x]; //i:32bit的首字节地址
//i是4的倍数的时候
if (i % Nk == 0)
{
/*字循环:循环左移1字节 RotWord()*/
t = temp[0]; temp[0] = temp[1]; temp[1] = temp[2]; temp[2] = temp[3]; temp[3] = t;
/*字节代换:SubWord()*/
for (x = 0; x < 4; x++)
{
temp[x] = sbox[temp[x]];
}
/*轮常量异或:Rcon[j]*/
temp[0] ^= Rcon[(i / Nk) - 1];
}
for (x = 0; x < 4; x++)
{
outkey[(4 * i) + x] = outkey[(4 * (i - Nk)) + x] ^ temp[x];
}
++i;
}
}
//定义轮密钥加操作
static void AddRoundKey(unsigned char* col, unsigned char* expansionkey, int round)//密匙加
{
//扩展密钥:44*32bit =11*4* 4*8 = 16字节*11轮,每轮用16字节密钥
//第0轮,只进行一次轮密钥加
//第1-10轮,轮密钥加
int x;
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++)
{ //每1轮操作:4*32bit密钥 = 16个字节密钥
col[x] ^= expansionkey[(round << 4) + x];
}
}
//AES加密函数
void AesEncrypt(unsigned char* blk, unsigned char* expansionkey, int Nr)
{//加密一个区块
//输入blk原文,直接在上面修改,输出blk密文
//输入skey:
//输入Nr = 10轮
int round;
//第1轮之前:轮密钥加
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, 0);
//第1-9轮:4类操作:字节代换、行移位、列混合、轮密钥加
for (round = 1; round <= (Nr - 1); round++)
{
SubBytes(blk); //输入16字节数组,直接在原数组上修改
ShiftRows(blk); //输入16字节数组,直接在原数组上修改
MixColumns(blk); //输入16字节数组,直接在原数组上修改
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, round);
}
//第10轮:不进行列混合
SubBytes(blk);
ShiftRows(blk);
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, Nr);
}
//AES 解密函数
void Contrary_AesEncrypt(unsigned char* blk, unsigned char* expansionkey, int Nr)
{
int x;
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, Nr);
Contrary_ShiftRows(blk);
Contrary_SubBytes(blk);
for (x = (Nr - 1); x >= 1; x--)
{
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, x);
Contrary_MixColumns(blk);
Contrary_ShiftRows(blk);
Contrary_SubBytes(blk);
}
AddRoundKey(blk, expansionkey, 0);
}
int main() {
unsigned char pt[32] = { 0x99, 0xE8, 0xB8, 0x01, 0xC8, 0x82, 0x51, 0x93, 0x12, 0xEE, 0x89, 0x64, 0xE7, 0xEF, 0x63, 0x8D, 0x51, 0xDF, 0x5D, 0x78, 0x39, 0xAA, 0x39, 0x62, 0xA0, 0xB4, 0x50, 0x30, 0x47, 0x30, 0x21, 0x06 };
unsigned char key[17] = "SYCLOVERSYCLOVER";
//定义pt数据
//定义密钥key
unsigned char expansionkey[15 * 16];
int i;
int j;
printf("You are welcome to use the AES machine in SDU\n");
printf("Please enter plaintext (length = 16):\n");
printf("please input key:\n");
//加密过程
ScheduleKey(key, expansionkey, 4, 10);//密钥扩展生成
//AesEncrypt(pt, expansionkey, 10);//调用AES 加密
printf("ciphertext: ");
//输出密文
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
printf("%02x ", pt[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
//解密过程
Contrary_AesEncrypt(pt, expansionkey, 10);//调用AES 解密
Contrary_AesEncrypt(&pt[16], expansionkey, 10);//调用AES 解密
printf("The decrypted plaintext is: ");
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
printf("%c", pt[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
while (1);
return 0;
}
base58可变表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int char_to_value(char c, const char* BASE58_ALPHABET) {
const char* p = strchr(BASE58_ALPHABET, c);
if (p) {
return p - BASE58_ALPHABET;
}
return -1;
}
//Base58解码函数
int base58_decode(const char* input, unsigned char* output, const char* BASE58_ALPHABET) {
size_t input_len = strlen(input);
int leading_zeros = 0;
while (leading_zeros < input_len && input[leading_zeros] == '1') {
leading_zeros++;
}
size_t result_size = (input_len * 733) / 1000 + 1; // 估算解码后的长度
uint8_t* result = (uint8_t*)malloc(result_size);
size_t result_index = 0;
for (size_t i = leading_zeros; i < input_len; i++) {
int carry = char_to_value(input[i], BASE58_ALPHABET);
if (carry == -1) {
free(result);
return -1;
}
for (size_t j = 0; j < result_index; j++) {
carry += (result[j] * 58);
result[j] = carry & 0xff;
carry >>= 8;
}
while (carry) {
result[result_index++] = carry & 0xff;
carry >>= 8;
}
}
//计算实际输出长度
size_t actual_output_len = leading_zeros + result_index;
//复制结果到输出缓冲区,并添加前导零
for (size_t i = 0; i < leading_zeros; i++) {
output[i] = 0;
}
for (size_t i = leading_zeros; i < actual_output_len; i++) {
output[i] = result[actual_output_len - i - 1];
}
free(result);
return 0;
}
//标准表
//123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyzbase85变表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define BASE85_TABLE_SIZE 85
unsigned long decode_char(char c, const char* base85_table) {
for (int i = 0; i < BASE85_TABLE_SIZE; ++i) {
if (c == base85_table[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
void decode_base85(const char* encoded_str, const char* base85_table, unsigned char* decoded_bytes) {
size_t encoded_len = strlen(encoded_str);
size_t decoded_index = 0;
unsigned long value = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < encoded_len; i += 5) {
value = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j) {
if (encoded_str[i + j] == '=') {
value *= 85;
}
else {
value = value * 85 + decode_char(encoded_str[i + j], base85_table);
}
}
for (int j = 3; j >= 0; --j) {
if (i + j < encoded_len && encoded_str[i + j] != '=') {
decoded_bytes[decoded_index++] = (value >> (8 * j)) & 0xFF;
}
}
}
}
//标准表
//!"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuFrida
在安装和升级的时候要注意,python、pip、frida、frida-tools的版本都要升级
adb connect 127.0.0.1:5555 #不同的模拟器ip不一定一样
adb -s 127.0.0.1:5555 shell
su
cd /data/local/tmp/
chomd 755 frida-server
./frida-server
adb forward tcp:27042 tcp:27042
adb forward tcp:27043 tcp:27043 #转发接听
frida-ps -U #输出列表就是OK了使用
#启动Frida
frida -U -f com.test.apk -l test.js --no-pause Cpython
分析XXX.so的时候先看,CreateStringTabAndInitStrings函数可以确定加载的特征
可以在linux上运行一下 dll的在windows上
from ctypes import *
a = cdll("./whereThelib.so")
a.c_func()
调试
Qemu调试
遇到过一个Linux arm架构需要调试的题目
qemu-arm-static -L ../ -g 12345 ./my_arm
// 监听端口 程序名称处理好后就可以直接使用ida进行attach附加 对程序进行调试了
随便写写
在函数调用的时候一般会 push rbp ; mov rbp,rsp ; sub rsp,??h
进行环境的储存和栈空间的分配,可以利用这个还原一定的SMC的密钥

Linux进入Anaconda环境
//进入环境
source ~/anaconda3/bin/activate
//查看现有虚拟环境
conda env list
//退出
conda deactivate通过x-python来模拟执行一个pyc文件
python2 -m xpython re3.pyc -v利用修改Manifest来使得软件在低版本中也可以被安装
//1、用apktool反编译
apktool d your_app.apk -o output_dir
在对lua进行反编译的时候 可以使用在线网站(据说更好用)
//使用luadec也可以达到相同的效果
luadec.exe data.lua > data_src.lua易语言可以通过对外部库的调用查看有无进行反调试
Tea 家族加密的时候如果将 i 融入进入加密过程中,要注意循环的倒序\
# 还原wxapkg文件可以运行js的脚本(试了好久环境变量配不上干脆直接绝对路径)
node C:\Users\hh\AppData\Roaming\npm\node_modules\wxapp-unpacker\wuWxapkg.js file.wxapkg
#如果加了混淆可以 deobfuscator 去掉混淆要是题目给出了一份完整的asm脚本,可以直接编译后放入ida
as re.asm -o tmp
gcc tmp -o out.exebc 文件通常指的是 Linux/Unix 下的 bc(Basic Calculator) 脚本文件
可以使用 clang baby.bc -o baby 将其编译为可执行文件
在使用 Z3进行求解的时候可能遇到 某几个值不同(比如说数独),而Z3的类型不能作为数组下标访问,3可以使用 Z3内置的 Distinct() 函数,用于表示内部的所有数不相同
for i in range(0, 25, 5):
S.add(Distinct(map[i], map[i+1], map[i+2], map[i+3], map[i+4]))
for j in range(5):
S.add(And(map[i+j] >= 1, map[i+j] <= 5))
# 注意如果使用for循环的简写进行写 Distinct 函数参数需要将 range 的返回进行解包
# S.add(Distinct(*[res[9*i+j] for j in range(8)]))